ESP8266 - Air Conditioner Command and Control Unit
This is part 2 of a series of posts where I'll try to show how I am trying to set up a home control and monitoring system using open source tools and network enabled sensors.
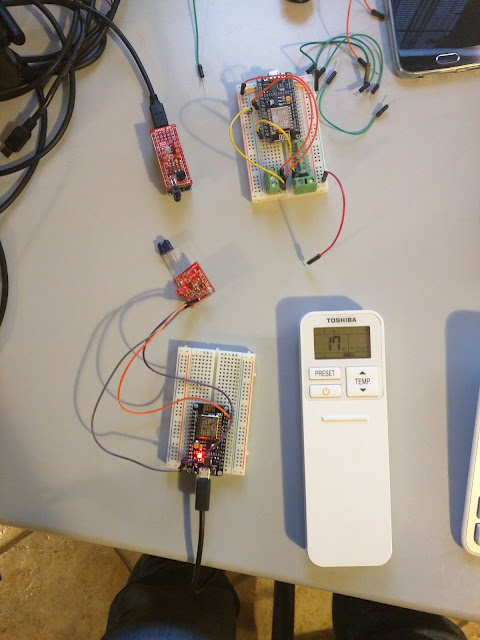
In Part 1 I illustrated how I decoded my Toshiba Air Conditioner AC signal, in this part I'll build on that to show how I built and ESP8266 based unit that is able to control five separate AC units in (hopefully in the near future) different rooms by receiving commands from a central server. The ESP8266 unit has also five DS18B20 temperature sensors that will be used to monitor real temperatures in the different rooms
Parts List:
- one ESP8266 based dev board, powered from USB, it has seven output pins available to control various sensors/modules, wifi capabilities and the NodeMcu firmware that allows normal arduino sketches to run on it
- 5 SendIR module: an arduino/esp8266 controllable module that has two high power/high range IR emitters, used to control AC units in different rooms Each module needs one pin to be controlled
- 5 DS18B20 temperature sensors: used to monitor temperatures in the rooms where the AC units will be installed
The photos are showing the dev board, with all sensors/modules connected locally, once the software side will be deemed stable they will be moved near the ac units from which I have ran cat5 cables that will be used to connect the sensors/shields to the ESP8266 board
Software:
- Arduino and NodeMcu firmware for the ESP8266 module
- Mosquitto: an open source MQTT broker. MQTT provides a lightweight method of carrying out messaging using a publish/subscribe model and it allows to connect different softwares with a standard approach
- openHAB: an open source home automation software, used to provide a web based interface to monitor and control the status of multiple sensors/units in a smart home
ESP8266 - One module to control it all
The ESP8266 module provides power to the five SendIr shields using the Vin pin (5v) and controls them using pins D0-D4. It also handles five temperature sensors using one single pin (SD2) and the Onewire library
The ESP8266 sends data and receive commands through a single connection to a MQTT server running on a Synology NAS, that also happens to run an instance of the home automation software (and an instance of an energy monitoring system, but that will be part 3 and 4 of the series) through Wifi.
The publisher/subscriber model of an MQTT server is pretty straightforward, the server allows clients to subscribe to topics and to send messages to specific topics:
What this allows to do in our case is for the ESP8266 to receive commands by other clients by subscribing to specific topics on the MQTT server, and also to send feedback about the state of the various AC units and temperatures to other MQTT topics, that will be consumed (read) by interested clients
This allows the home automation software to generate commands to control the AC units in different rooms without knowing anything about IR signals and IR protocols, the only thing that it knows is that in order for, say, turn on an AC unit in room1 it is necessary to send the message "1" to the topic "esp8266/01/in/00/00". This message will be received by the ESP8266 unit that will convert the information into the appropriate IR signal that will be sent to the appropriate AC unit
The ESP8266 Sketch:
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <OneWire.h>
#include <DallasTemperature.h>
#include <PubSubClient.h>
//Def
#define HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG; // Un comment to access DEBUG information through Serial Interface
#define ONE_WIRE_BUS 10 // DS18B20 on arduino pin10 corresponds to SD3 on ESP8266 Dev Board
#define NUMROOMS 5
#define DELAY 60000 //Check temp every 10 sec
int ledPin = 2; // GPIO2
WiFiClient espClient;
PubSubClient client(espClient);
OneWire oneWire(ONE_WIRE_BUS);
DallasTemperature DS18B20(&oneWire);
float prevTemp = 0;
const char* MY_SSID = "WIFISSID";
const char* MY_PWD = "WIFIPWD";
int sent = 0;
char mqtt_user[] = "mqttuser";
char mqtt_password[] = "mqttpasswd";
char mqtt_id[] = "esp8266-01";
const char* mqtt_server = "ipoftheserver";
const char * outTopic = "esp8266/01/out";
const char * pingTopic = "esp8266/01/ping";
char * statusTopic = "esp8266/01/status/00/00";
char * inTopic = "esp8266/01/in/#";
typedef struct roomHvac RoomHvac;
unsigned long nextPingOn = 0;
unsigned long pingDelay = 60000;
byte probes[][8] = {
{ 0x28, 0x82, 0xEB, 0x35, 0x05, 0x00, 0x00, 0xCC },
{ 0x28, 0xDD, 0x1F, 0x35, 0x05, 0x00, 0x00, 0x7F },
{ 0x28, 0xB7, 0x8B, 0x34, 0x05, 0x00, 0x00, 0x54 },
{ 0x28, 0x2B, 0x4C, 0x35, 0x05, 0x00, 0x00, 0x64 },
{ 0x28, 0x4F, 0xC3, 0xA2, 0x04, 0x00, 0x00, 0x13 }
};
float drift[5] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0};
// Reconnect to the MQTT server in case of disconnect
void reconnect() {
// Loop until we're reconnected
while (!client.connected()) {
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.println("Attempting MQTT reconnection...");
#endif
if (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED)
{
connectWifi();
}
// Attempt to connect
if (client.connect(mqtt_id, mqtt_user, mqtt_password)) {
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.println("reconnected");
#endif
// Once connected, publish an announcement...
client.publish(pingTopic, "2");
// ... and resubscribe
client.subscribe(inTopic);
} else {
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.print("failed, rc=");
Serial.print(client.state());
Serial.println(" try again in 5 seconds");
// Wait 5 seconds before retrying
#endif
delay(15000);
}
}
}
int halfPeriodicTime;
int IRpin;
int khz;
typedef enum HvacMode {
HVAC_HOT,
HVAC_COLD,
HVAC_DRY,
HVAC_FAN, // used for Panasonic only
HVAC_AUTO
} HvacMode_t; // HVAC MODE
typedef enum HvacFanMode {
FAN_SPEED_1,
FAN_SPEED_2,
FAN_SPEED_3,
FAN_SPEED_4,
FAN_SPEED_5,
FAN_SPEED_AUTO,
FAN_SPEED_SILENT
} HvacFanMode_; // HVAC FAN MODE
typedef enum HvacVanneMode {
VANNE_AUTO,
VANNE_H1,
VANNE_H2,
VANNE_H3,
VANNE_H4,
VANNE_H5,
VANNE_AUTO_MOVE
} HvacVanneMode_; // HVAC VANNE MODE
typedef enum HvacWideVanneMode {
WIDE_LEFT_END,
WIDE_LEFT,
WIDE_MIDDLE,
WIDE_RIGHT,
WIDE_RIGHT_END
} HvacWideVanneMode_t; // HVAC WIDE VANNE MODE
typedef enum HvacAreaMode {
AREA_SWING,
AREA_LEFT,
AREA_AUTO,
AREA_RIGHT
} HvacAreaMode_t; // HVAC WIDE VANNE MODE
typedef enum HvacProfileMode {
NORMAL,
QUIET,
BOOST
} HvacProfileMode_t; // HVAC PANASONIC OPTION MODE
struct roomHvac
{
int temp;
int state; // 0 - OFF 1 - ON
HvacFanMode fanHvac;
HvacMode modeHvac;
int pin;
float probeTemp;
float oldTemp;
};
void sendHvacToshiba(
HvacMode ,
int ,
HvacFanMode ,
int ,
int
);
typedef struct roomHvac RoomHvac;
RoomHvac rooms[NUMROOMS];
void publishRoomStatus(int roomNo) {
char b[10];
statusTopic[19] = '0' + roomNo;
statusTopic[22] = '0';
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.print("Sending update for room ");
Serial.println(roomNo);
Serial.println();
#endif
sprintf(b, "%d", rooms[roomNo].state);
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.print("Publishing value ");
Serial.print(b);
Serial.print(" to Topic: ");
Serial.println(statusTopic);
#endif
client.publish(statusTopic, b);
statusTopic[22] = '1';
sprintf(b, "%d", rooms[roomNo].temp);
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.print("Publishing value ");
Serial.print(b);
Serial.print(" to Topic: ");
Serial.println(statusTopic);
#endif
client.publish(statusTopic, b);
statusTopic[22] = '2';
sprintf(b, "%d", (int)rooms[roomNo].modeHvac);
client.publish(statusTopic, b);
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.print("Publishing value ");
Serial.print(b);
Serial.print(" to Topic: ");
Serial.println(statusTopic);
#endif
statusTopic[22] = '3';
sprintf(b, "%d", (int)rooms[roomNo].fanHvac);
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.print("Publishing value ");
Serial.print(b);
Serial.print(" to Topic: ");
Serial.println(statusTopic);
#endif
client.publish(statusTopic, b);
statusTopic[22] = '4';
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.print("Publishing value ");
Serial.print(rooms[roomNo].probeTemp);
Serial.print(" to Topic: ");
Serial.println(statusTopic);
#endif
client.publish(statusTopic, f2s(rooms[roomNo].probeTemp, 2));
}
void callback(char* topic, byte* payload, unsigned int length) {
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.print("Message arrived [");
Serial.print(topic);
Serial.print("] ");
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Serial.print((char)payload[i]);
}
Serial.println();
#endif
payload[length] = '\0';
int val = atoi((char *)payload);
client.publish(outTopic, "received");
int roomNo = (int)topic[15] - 48;
char commandRoom = topic[18];
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.print("Received command for room:");
Serial.println(roomNo);
Serial.print("Received command:");
Serial.println(commandRoom);
Serial.print("Received val:");
Serial.println(val);
#endif
/*
Rooms:
0: Sala
1: Studio
2: Camera PT
3: Camera NORD PP
4: Camera SUD PP
Commands:
0: 0 = OFF 1 = ON
1: TEMP SETPOINT (17-30)
2: AC MODE: 0: Hot 1: Cold 2: Dry 4: Auto
3: FAN Mode: 0: 1 1: 2 2:3 3: 4 4: 5 5: AUTO
*/
if (roomNo >= 0 && roomNo <= NUMROOMS - 1 ) {
switch (commandRoom) {
case '0':
if (val == 0 || val == 1) {
rooms[roomNo].state = val;
}
break;
case '1':
if (val < 17) {
val = 17;
}
if (val > 30) {
val = 30;
}
rooms[roomNo].temp = val;
break;
case '2':
if (val >= 0 && val <= 4) {
rooms[roomNo].modeHvac = (HvacMode) val;
}
break;
case '3':
if (val >= 0 && val <= 5) {
rooms[roomNo].fanHvac = (HvacFanMode)val;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.println("Room Data:");
Serial.print("State: ");
Serial.println(rooms[roomNo].state);
Serial.print("Temp: ");
Serial.println(rooms[roomNo].temp);
Serial.print("Mode: ");
Serial.println(rooms[roomNo].modeHvac);
Serial.print("Fan: ");
Serial.println(rooms[roomNo].fanHvac);
#endif
int offState = 0;
if ( rooms[roomNo].state == 0) {
offState = 1;
}
sendHvacToshiba(rooms[roomNo].modeHvac, rooms[roomNo].temp, rooms[roomNo].fanHvac, offState, rooms[roomNo].pin);
//const char * statusTopic="esp8266/01/status/00/00";
publishRoomStatus(roomNo);
}
}
// HVAC TOSHIBA_
#define HVAC_TOSHIBA_HDR_MARK 4400
#define HVAC_TOSHIBA_HDR_SPACE 4300
#define HVAC_TOSHIBA_BIT_MARK 560
#define HVAC_TOSHIBA_ONE_SPACE 1590
#define HVAC_MISTUBISHI_ZERO_SPACE 472
#define HVAC_TOSHIBA_RPT_MARK 440
#define HVAC_TOSHIBA_RPT_SPACE 7048 // Above original iremote limit
/****************************************************************************
/* Send IR command to Toshiba HVAC - sendHvacToshiba
/***************************************************************************/
void sendHvacToshiba(
HvacMode HVAC_Mode, // Example HVAC_HOT
int HVAC_Temp, // Example 21 (°c)
HvacFanMode HVAC_FanMode, // Example FAN_SPEED_AUTO
int OFF, // Example false
int irPin
)
{
#define HVAC_TOSHIBA_DATALEN 9
IRpin = irPin;
byte mask = 1; //our bitmask
//F20D03FC0150000051
byte data[HVAC_TOSHIBA_DATALEN] = { 0xF2, 0x0D, 0x03, 0xFC, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 };
// data array is a valid trame, only byte to be chnaged will be updated.
byte i;
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.println("Packet to send: ");
for (i = 0; i < HVAC_TOSHIBA_DATALEN; i++) {
Serial.print("_");
Serial.print(data[i], HEX);
}
Serial.println(".");
#endif
data[6] = 0x00;
// Byte 7 - Mode
switch (HVAC_Mode)
{
case HVAC_HOT: data[6] = (byte) B00000011; break;
case HVAC_COLD: data[6] = (byte) B00000001; break;
case HVAC_DRY: data[6] = (byte) B00000010; break;
case HVAC_AUTO: data[6] = (byte) B00000000; break;
default: break;
}
// Byte 7 - On / Off
if (OFF) {
data[6] = (byte) 0x07; // Turn OFF HVAC
} else {
// Turn ON HVAC (default)
}
// Byte 6 - Temperature
// Check Min Max For Hot Mode
byte Temp;
if (HVAC_Temp > 30) {
Temp = 30;
}
else if (HVAC_Temp < 17) {
Temp = 17;
}
else {
Temp = HVAC_Temp;
};
data[5] = (byte) Temp - 17 << 4;
// Byte 10 - FAN / VANNE
switch (HVAC_FanMode)
{
case FAN_SPEED_1: data[6] = data[6] | (byte) B01000000; break;
case FAN_SPEED_2: data[6] = data[6] | (byte) B01100000; break;
case FAN_SPEED_3: data[6] = data[6] | (byte) B10000000; break;
case FAN_SPEED_4: data[6] = data[6] | (byte) B10100000; break;
case FAN_SPEED_5: data[6] = data[6] | (byte) B11000000; break;
case FAN_SPEED_AUTO: data[6] = data[6] | (byte) B00000000; break;
case FAN_SPEED_SILENT: data[6] = data[6] | (byte) B00000000; break;//No FAN speed SILENT for TOSHIBA so it is consider as Speed AUTO
default: break;
}
// Byte 9 - CRC
data[8] = 0;
for (i = 0; i < HVAC_TOSHIBA_DATALEN - 1; i++) {
data[HVAC_TOSHIBA_DATALEN - 1] = (byte) data[i] ^ data[HVAC_TOSHIBA_DATALEN - 1]; // CRC is a simple bits addition
}
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.println("Packet to send: ");
for (i = 0; i < HVAC_TOSHIBA_DATALEN; i++) {
Serial.print("_"); Serial.print(data[i], HEX);
}
Serial.println(".");
for (i = 0; i < HVAC_TOSHIBA_DATALEN ; i++) {
Serial.print(data[i], BIN); Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println(".");
#endif
enableIROut(38); // 38khz
space(0);
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) { // For Toshiba IR protocol we have to send two time the packet data
// Header for the Packet
mark(HVAC_TOSHIBA_HDR_MARK);
space(HVAC_TOSHIBA_HDR_SPACE);
for (i = 0; i < HVAC_TOSHIBA_DATALEN; i++) {
// Send all Bits from Byte Data in Forward Order (MSB)
for (mask = 10000000; mask > 0; mask >>= 1) { //iterate through bit mask
if (data[i] & mask) { // Bit ONE
mark(HVAC_TOSHIBA_BIT_MARK);
space(HVAC_TOSHIBA_ONE_SPACE);
}
else { // Bit ZERO
mark(HVAC_TOSHIBA_BIT_MARK);
space(HVAC_MISTUBISHI_ZERO_SPACE);
}
//Next bits
}
}
// End of Packet and retransmission of the Packet
mark(HVAC_TOSHIBA_RPT_MARK);
space(HVAC_TOSHIBA_RPT_SPACE);
space(0); // Just to be sure
}
}
/****************************************************************************
/* enableIROut : Set global Variable for Frequency IR Emission
/***************************************************************************/
void enableIROut(int khz) {
// Enables IR output. The khz value controls the modulation frequency in kilohertz.
halfPeriodicTime = 500 / khz; // T = 1/f but we need T/2 in microsecond and f is in kHz
}
/****************************************************************************
/* mark ( int time)
/***************************************************************************/
void mark(int time) {
// Sends an IR mark for the specified number of microseconds.
// The mark output is modulated at the PWM frequency.
long beginning = micros();
while (micros() - beginning < time) {
digitalWrite(IRpin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(halfPeriodicTime);
digitalWrite(IRpin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(halfPeriodicTime); //38 kHz -> T = 26.31 microsec (periodic time), half of it is 13
}
}
/****************************************************************************
/* space ( int time)
/***************************************************************************/
/* Leave pin off for time (given in microseconds) */
void space(int time) {
// Sends an IR space for the specified number of microseconds.
// A space is no output, so the PWM output is disabled.
digitalWrite(IRpin, LOW);
if (time > 0) delayMicroseconds(time);
}
/****************************************************************************
/* sendRaw (unsigned int buf[], int len, int hz)
/***************************************************************************/
void sendRaw (unsigned int buf[], int len, int hz)
{
enableIROut(hz);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (i & 1) {
space(buf[i]);
}
else {
mark(buf[i]);
}
}
space(0); // Just to be sure
}
/* Check the temperature data */
void tempTimer() {
//Getting the temperature
float temp = 0;
for (int r = 0; r < NUMROOMS; r++) {
rooms[r].oldTemp = rooms[r].probeTemp;
rooms[r].probeTemp = readTemp(probes[r]) - drift[r];
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.print("Room: ");
Serial.print(r);
Serial.print(" - Temperature: ");
Serial.println(rooms[r].probeTemp);
#endif
if (rooms[r].probeTemp != rooms[r].oldTemp) {
publishRoomStatus(r);
}
}
}
/* float to string
f is the float to turn into a string
p is the precision (number of decimals)
return a string representation of the float.
*/
char *f2s(float f, int p) {
char * pBuff; // use to remember which part of the buffer to use for dtostrf
const int iSize = 10; // number of bufffers, one for each float before wrapping around
static char sBuff[iSize][20]; // space for 20 characters including NULL terminator for each float
static int iCount = 0; // keep a tab of next place in sBuff to use
pBuff = sBuff[iCount]; // use this buffer
if (iCount >= iSize - 1) { // check for wrap
iCount = 0; // if wrapping start again and reset
}
else {
iCount++; // advance the counter
}
return dtostrf(f, 0, p, pBuff); // call the library function
}
void setup() {
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Sketch Started.");
#endif
IRpin = D0;
khz = 38;
halfPeriodicTime = 500 / khz;
pinMode(IRpin, OUTPUT);
for (int r = 0; r < NUMROOMS; r++) {
/*
struct roomHvac
{
int temp;
int state; // 0 - OFF 1 - ON
HvacFanMode fanHvac;
HvacMode modeHvac;
};
*/
rooms[r].temp = 22;
rooms[r].state = 0;
rooms[r].fanHvac = FAN_SPEED_AUTO;
rooms[r].modeHvac = HVAC_AUTO;
}
rooms[0].pin = D0;
pinMode(D0, OUTPUT);
rooms[1].pin = D1;
pinMode(D1, OUTPUT);
rooms[2].pin = D2;
pinMode(D2, OUTPUT);
rooms[3].pin = D3;
pinMode(D3, OUTPUT);
rooms[4].pin = D4;
pinMode(D4, OUTPUT);
connectWifi();
client.setServer(mqtt_server, 1883);
client.setCallback(callback);
if (client.connect(mqtt_id, mqtt_user, mqtt_password)) {
client.publish(outTopic, "hello world");
client.subscribe(inTopic);
}
for (int r = 0; r < 5; r++) {
publishRoomStatus(r);
}
}
void loop() {
float temp;
if (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED)
{
connectWifi();
}
if (!client.connected()) {
reconnect();
}
client.loop();
unsigned long time = millis();
if (time > nextPingOn) {
tempTimer();
client.publish(pingTopic, "1");
nextPingOn = time + pingDelay;
}
}
void connectWifi()
{
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.print("Connecting to " + *MY_SSID);
#endif
WiFi.begin(MY_SSID, MY_PWD);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(1000);
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.print(".");
#endif
}
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Connected to ");
Serial.println(MY_SSID);
Serial.print("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
#endif
}//end connect
float readTemp(byte *addressDs1820) {
byte i;
byte present = 0;
byte type_s;
byte data[12];
byte *addr;
float celsius;
/*
if ( !ds.search(addr)) {
ds.reset_search();
delay(250);
return;
}
*/
addr = addressDs1820;
if (OneWire::crc8(addr, 7) != addr[7]) {
return -1;
}
// the first ROM byte indicates which chip
switch (addr[0]) {
case 0x10:
type_s = 1;
break;
case 0x28:
type_s = 0;
break;
case 0x22:
type_s = 0;
break;
default:
return -1;
}
oneWire.reset();
oneWire.select(addr);
oneWire.write(0x44, 1); // start conversion, with parasite power on at the end
delay(1000); // maybe 750ms is enough, maybe not
// we might do a ds.depower() here, but the reset will take care of it.
present = oneWire.reset();
oneWire.select(addr);
oneWire.write(0xBE); // Read Scratchpad
for ( i = 0; i < 9; i++) { // we need 9 bytes
data[i] = oneWire.read();
}
// Convert the data to actual temperature
// because the result is a 16 bit signed integer, it should
// be stored to an "int16_t" type, which is always 16 bits
// even when compiled on a 32 bit processor.
int16_t raw = (data[1] << 8) | data[0];
if (type_s) {
raw = raw << 3; // 9 bit resolution default
if (data[7] == 0x10) {
// "count remain" gives full 12 bit resolution
raw = (raw & 0xFFF0) + 12 - data[6];
}
} else {
byte cfg = (data[4] & 0x60);
// at lower res, the low bits are undefined, so let's zero them
if (cfg == 0x00) raw = raw & ~7; // 9 bit resolution, 93.75 ms
else if (cfg == 0x20) raw = raw & ~3; // 10 bit res, 187.5 ms
else if (cfg == 0x40) raw = raw & ~1; // 11 bit res, 375 ms
//// default is 12 bit resolution, 750 ms conversion time
}
celsius = (float)raw / 16.0;
// fahrenheit = celsius * 1.8 + 32.0;
return celsius;
}
The sketch uses the following data structures:
roomHvac:
structure that hold information about a room AC and temp status, I have defined a fixed size in function of the number of rooms/AC in my house
roomHvac:
struct roomHvac
{
int temp;
int state; // 0 - OFF 1 - ON
HvacFanMode fanHvac;
HvacMode modeHvac;
int pin;
float probeTemp;
float oldTemp;
}; structure that hold information about a room AC and temp status, I have defined a fixed size in function of the number of rooms/AC in my house
probes:
This structure holds the physical addresses of the temperature sensors, detected by connecting them one at a time and running this sketch on the ESP8266:
byte probes[][8] = {
{ 0x28, 0x82, 0xEB, 0x35, 0x05, 0x00, 0x00, 0xCC },
{ 0x28, 0xDD, 0x1F, 0x35, 0x05, 0x00, 0x00, 0x7F },
{ 0x28, 0xB7, 0x8B, 0x34, 0x05, 0x00, 0x00, 0x54 },
{ 0x28, 0x2B, 0x4C, 0x35, 0x05, 0x00, 0x00, 0x64 },
{ 0x28, 0x4F, 0xC3, 0xA2, 0x04, 0x00, 0x00, 0x13 }
}; This structure holds the physical addresses of the temperature sensors, detected by connecting them one at a time and running this sketch on the ESP8266:
#include// OneWire-Bibliothek einbinden #include // DS18B20-Bibliothek einbinden #define DS18B20_PIN 10 // Pin für DS18B20 definieren Arduino D2 OneWire ds(DS18B20_PIN); // Connect your 1-wire device to pin 3 void setup(void) { Serial.begin(115200); discoverOneWireDevices(); } void discoverOneWireDevices(void) { byte i; byte present = 0; byte data[12]; byte addr[8]; Serial.print("Looking for 1-Wire devices...\n\r"); while(ds.search(addr)) { Serial.print("\n\rFound \'1-Wire\' device with address:\n\r"); for( i = 0; i < 8; i++) { Serial.print("0x"); if (addr[i] < 16) { Serial.print('0'); } Serial.print(addr[i], HEX); if (i < 7) { Serial.print(", "); } } if ( OneWire::crc8( addr, 7) != addr[7]) { Serial.print("CRC is not valid!\n"); return; } } Serial.print("\n\r\n\rThat's it.\r\n"); ds.reset_search(); return; } void loop(void) { // nothing to see here }
MQTT:
char mqtt_user[] = "mqttuser";
char mqtt_password[] = "mqttpasswd";
char mqtt_id[] = "esp8266-01";
const char* mqtt_server = "ipoftheserver";
const char * outTopic = "esp8266/01/out";
const char * pingTopic = "esp8266/01/ping";
char * statusTopic = "esp8266/01/status/00/00";
char * inTopic = "esp8266/01/in/#";
these variables define the connection parameters to the MQTT server and the topics used to communicate with other clients, the ESP8266 will react to any message published on the topics with base address "esp8266/01/in/#" and every time it will change any parameter for a specific room it will publish a status packet on the appropriate "esp8266/01/status/0x/0x" topic. It will also publish a ping message once every minute (will be used to monitor for failures on the server side)
The function where all logic conversion between messages published on the topics and commands sent to the ac units is the callback function:
void callback(char* topic, byte* payload, unsigned int length) {
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.print("Message arrived [");
Serial.print(topic);
Serial.print("] ");
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Serial.print((char)payload[i]);
}
Serial.println();
#endif
payload[length] = '\0';
int val = atoi((char *)payload);
client.publish(outTopic, "received");
int roomNo = (int)topic[15] - 48;
char commandRoom = topic[18];
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.print("Received command for room:");
Serial.println(roomNo);
Serial.print("Received command:");
Serial.println(commandRoom);
Serial.print("Received val:");
Serial.println(val);
#endif
/*
Rooms:
0: Sala
1: Studio
2: Camera PT
3: Camera NORD PP
4: Camera SUD PP
Commands:
0: 0 = OFF 1 = ON
1: TEMP SETPOINT (17-30)
2: AC MODE: 0: Hot 1: Cold 2: Dry 4: Auto
3: FAN Mode: 0: 1 1: 2 2:3 3: 4 4: 5 5: AUTO
*/
if (roomNo >= 0 && roomNo <= NUMROOMS - 1 ) {
switch (commandRoom) {
case '0':
if (val == 0 || val == 1) {
rooms[roomNo].state = val;
}
break;
case '1':
if (val < 17) {
val = 17;
}
if (val > 30) {
val = 30;
}
rooms[roomNo].temp = val;
break;
case '2':
if (val >= 0 && val <= 4) {
rooms[roomNo].modeHvac = (HvacMode) val;
}
break;
case '3':
if (val >= 0 && val <= 5) {
rooms[roomNo].fanHvac = (HvacFanMode)val;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
#ifdef HVAC_TOSHIBA_DEBUG
Serial.println("Room Data:");
Serial.print("State: ");
Serial.println(rooms[roomNo].state);
Serial.print("Temp: ");
Serial.println(rooms[roomNo].temp);
Serial.print("Mode: ");
Serial.println(rooms[roomNo].modeHvac);
Serial.print("Fan: ");
Serial.println(rooms[roomNo].fanHvac);
#endif
int offState = 0;
if ( rooms[roomNo].state == 0) {
offState = 1;
}
sendHvacToshiba(rooms[roomNo].modeHvac, rooms[roomNo].temp, rooms[roomNo].fanHvac, offState, rooms[roomNo].pin);
//const char * statusTopic="esp8266/01/status/00/00";
publishRoomStatus(roomNo);
}
}
.. to be continued ...








Commenti
air duct cleaning palatine
mining machines air conditioning repair Ireland
duct cleaning buffalo grove
Ducted Air Conditioning Sydney
https://khetigaadi.com/new-tractor-brand/sonalika/en
NEBOSH IGC Course
Posta un commento